Windows 10 includes a new feature called Windows Update Delivery Optimization that can download updates from other PCs instead of directly from Microsoft servers. This can be beneficial if you have multiple Windows 10 computers on your local network because it reduces the amount of data transfer on your Internet connection. After a Windows 10 PC downloads an update, it can share the update with other computers in your home instead of downloading additional copies over the Internet. This is an awesome new feature that can help users save bandwidth, especially those on metered or slow internet connections. But there is one aspect of this feature I wish Microsoft disabled by default.
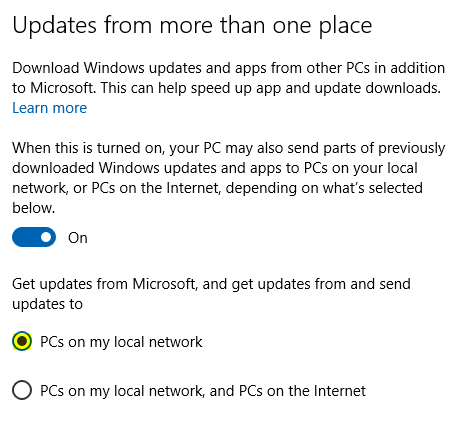
On Windows 10 and Windows 10 Pro editions, the Windows Update Delivery Optimization feature is configured to share updates with PCs on your local network and with other computers on the Internet. That means your PC could be sharing Windows Updates to other people's Windows 10 PCs around the world, using your Internet Connection bandwidth.
Microsoft says Windows 10 automatically disables this feature if it detects or you designate a connection as metered. But how exactly does Windows accurately detect if a connection is billed based on usage? And how many of you with metered connections knew this feature even existed before reading this article and designated your connection as metered?
Users of Windows 10 Enterprise and Education have nothing to worry about as those editions have the sharing of updates over the Internet disabled by default. But most consumers run Windows 10 or Windows 10 Pro and must explicitly disable this feature by following these steps:
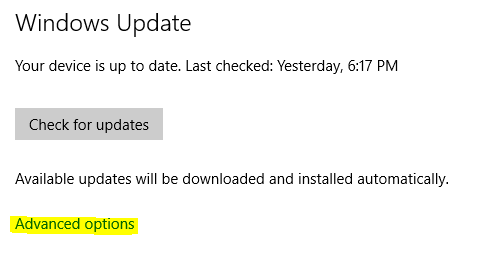
1. Click on the Start Button and type in Windows Update and hit Enter.
2. On the Windows Update screen, click on Advanced options.
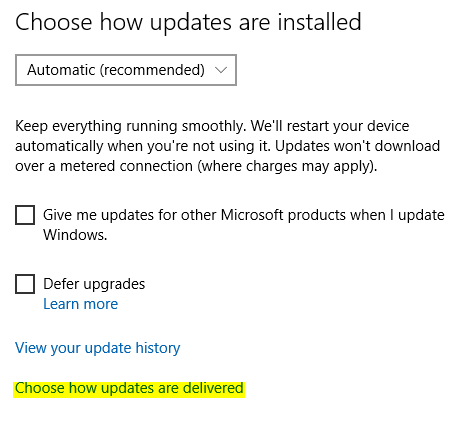
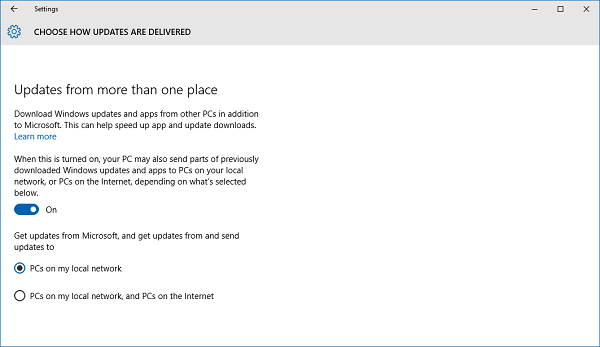
3. Under Chose how updates are installed, click on Choose how updates are delivered.
4. Select PCs on my local network to ensure updates are only sent to your computers.
That's It! Now you can benefit from this awesome feature without the negative aspects.
If you would like to learn more about the Windows Update Delivery Optimization feature, check out the Microsoft FAQ.